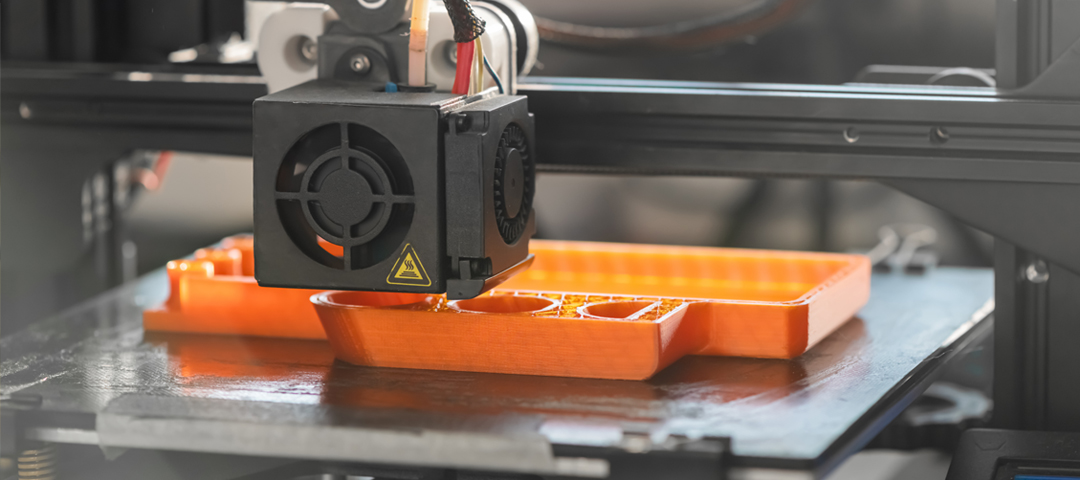
3D printing process and 3D printing services
3D printing process
Molten deposition modeling: This is the most common and widely used 3D printing process. It uses thermoplastic materials (such as plastic wire) to build objects by heating and extruding them layer by layer. The printing head heats the material to a molten state, and then constructs the object by controlling the movement of the printing head.
Light curing: This process uses liquid photosensitive resin to construct objects by layer curing using ultraviolet lasers or similar light sources. The beam of light illuminates the liquid resin, causing it to solidify into a solid. The printing platform gradually moves upwards, and after each layer solidifies, the solid layer formed adheres to the previous layer.
Selective laser sintering: This process uses powder materials (such as nylon, metal powder, etc.) to construct objects by layer sintering using a laser beam. The laser beam scans and sinters the powder, connecting it with the previous layer to form a solid object. Unsintered powder can be used as a support structure to support the printing process.
Electron beam melting: This process is similar to SLS, but uses an electron beam instead of a laser beam. The electron beam irradiates metal powder, melts it and stacks it layer by layer to form a solid object. EBM is typically used for metal 3D printing.
Inkjet printing: This process uses a nozzle similar to an inkjet printer, which sprays liquid materials layer by layer onto the printing platform to construct objects. Ink jet printing is commonly used for bioprinting and printing complex color models.
Other 3D printing processes, such as electrochemical printing, clay printing, bioprinting, etc. Each process has its specific advantages and applicability, and it is important to choose the appropriate process based on printing needs and materials to be printed.
3D printing and rapid prototyping manufacturing
3D printing and rapid prototyping manufacturing are innovative technologies in the field of modern manufacturing, with many similarities.
3D printing
3D printing is a manufacturing technique that creates objects by stacking materials layer by layer. It uses computer-aided design (CAD) software to convert digital models into printable files.
It is mainly divided into several types, including melt deposition modeling (FDM), light curing (SLA/DLP), selective laser sintering (SLS), electron beam melting (EBM), etc.
Different types of materials can be used, such as plastic, metal, ceramics, etc., to achieve 3D printing. Materials can be traditional or special functional materials.
Rapid prototyping manufacturing:
Rapid prototyping manufacturing is a broad manufacturing technology that includes 3D printing. Implement rapid manufacturing of products through a series of rapid manufacturing and prototyping technologies.
Rapid prototyping manufacturing technology includes various technologies such as 3D printing, laser cutting, CNC machining, and injection molding. These technologies can quickly produce products or prototypes.
The advantage of rapid prototyping manufacturing technology lies in its ability to quickly and flexibly manufacture complex shaped products without the need for traditional process flow and a large amount of manual intervention.
Common features
Both 3D printing and rapid prototyping manufacturing have the characteristics of rapid manufacturing, which can produce products or prototypes in a short period of time.
Both can achieve customized production and manufacture personalized products according to customer needs.
Both 3D printing and rapid prototyping manufacturing can achieve the manufacturing of complex shapes, including internal cavities, geometrically complex structures, etc.
3D printing and rapid prototyping manufacturing are innovative technologies in modern manufacturing that can quickly and flexibly manufacture complex shaped products to meet customization needs. These technologies are widely used in many industries, such as aerospace, medical, automotive, consumer goods, etc.
What materials can be used for 3D printing?
Plastic
The most commonly used materials for 3D printing are various plastics. This includes polymer materials such as polyethylene, polypropylene, polylactic acid, polycarbonate, nylon, etc.
Different plastic materials have different characteristics, such as strength, heat resistance, chemical resistance, etc. This makes plastic an ideal choice for manufacturing prototypes and small-scale production.
Metal
Metal materials can also be used for 3D printing, known as metal 3D printing. Commonly used metal materials include stainless steel, aluminum alloy, titanium alloy, nickel alloy, etc.The technology used for metal 3D printing is usually Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) or Direct Energy Deposition (DED), which constructs metal objects by melting metal powders or wires with lasers or arcs.
Ceramics
Ceramic materials can be used to manufacture parts or appliances with high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance. Common ceramic materials include alumina, silicon nitride, silicon carbide, etc.Ceramic 3D printing usually uses laser solidification or powder sintering technology to solidify or sinter ceramic powder layer by layer to construct objects.
Biomaterials
Biomaterials are used for three-dimensional printing applications in the biomedical field, such as bioprinting tissues and organs. Common biomaterials include bioprinting ink, bioceramics, biological scaffolds, etc.
There are also other materials that can be used for 3D printing, such as gypsum, paper, food materials, etc. With the continuous development of technology, new materials are also emerging, expanding the application fields and possibilities of 3D printing. The selection of suitable materials depends on the printing purpose, required characteristics, and limitations of printing technology.
How long does 3D printing take?
The time required for 3D printing depends on multiple factors. More complex models typically require longer printing time because they require more layers and details.
Different 3D printers have different printing speeds. Some high-end printers can complete printing tasks faster, while low-end printers may take longer.
The thickness of the printing layer determines the time required for each layer. A thinner layer thickness will increase printing time as more layers need to be printed.
Different printing materials have different characteristics, such as melting point and curing time. These characteristics can affect printing time.
The time for 3D printing can range from a few minutes to several days. For smaller and simpler models, the printing time may only take a few minutes or hours. For large and complex models, the printing time may take tens of hours or even longer.
3D printing services
Prototyping
Many companies and designers use 3D printing services to create product prototypes. Customers can provide design files or models, and then use professional 3D printing equipment to print them into physical models for testing, evaluation, and display.
Customized products
3D printing technology makes it possible to manufacture personalized and customized products. Through 3D printing services, customers can customize the appearance, size, material, etc. of their products according to their own needs and requirements, and obtain unique products.
Mass production
For small-scale production or production with specific needs, 3D printing services also provide a flexible choice. Customers can use 3D printing services to mass produce products without the need to invest a large amount of equipment and human resources.
Education and research
Schools, universities, and research institutions can utilize 3D printing services for education and research. This includes creating teaching models, experimental equipment, simulation models, etc. to support teaching and research activities.
 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Email
Email
 Get a Auota
Get a Auota